增材制造,通常称为3D打印,正在革新工业格局。随着各行业追求效率和创新,对先进制造技术的需求正在增加。然而,这项技术的快速发展带来了必须解决的挑战,以充分发挥其潜力。
快速修复总结表
| 问题 | Quick Fix | 长期解决方案 | 影响 | 示例行业 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High material costs | 使用回收材料 | 开发成本效益高的材料 | Reduced production costs | 汽车 |
| 多材料能力有限 | Invest in hybrid printers | 材料兼容性研究 | Enhanced product functionality | 航空航天 |
| 生产速度缓慢 | Optimize printing parameters | 开发更快的打印技术 | 提高产量 | Consumer Electronics |
| 设计复杂性限制 | 使用AI驱动的设计工具 | Develop advanced CAD software | 更大的设计灵活性 | 医疗设备 |
| Lack of skilled workforce | 实施培训计划 | 集成AI进行自动化 | Increased efficiency and innovation | 一般制造业 |
工业3D打印
工业3D打印是增材制造的一个子集,正在改变各个行业的生产流程。与传统制造通常涉及的减材工艺不同,3D打印通过逐层构建物体来减少浪费并实现复杂的几何形状。这项技术对于需要定制化解决方案的行业特别有益,如航空航天、汽车和医疗保健。
工业3D打印的优势:
- Customization and Complexity: Industrial 3D printing allows for the creation of complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability is particularly valuable in industries like aerospace, where intricate designs can lead to improved performance and efficiency.
- Reduced Waste: Traditional manufacturing processes often result in significant material waste. In contrast, additive manufacturing uses only the material necessary to build an object, leading to more sustainable production practices.
- Rapid Prototyping and Production: The ability to quickly produce prototypes accelerates the design and testing phases of product development. This speed also translates to faster production times for end-use parts, reducing time-to-market.
- Cost Efficiency for Low Volume Production: For small batch productions, 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional methods, which often require expensive tooling and setup.
- Supply Chain Simplification: By enabling on-demand production, 3D printing can reduce the need for large inventories and complex supply chains, lowering costs and increasing responsiveness to market demands.
工业3D打印的挑战:
尽管具有优势,工业3D打印仍面临若干挑战。与传统方法相比,高昂的材料成本、有限的材料选择和较慢的生产速度可能阻碍其广泛采用。此外,质量控制和标准化仍然是重大障碍。
比较表:工业与原型3D打印
| 功能 | Industrial 3D Printing | 原型3D打印 |
|---|---|---|
| 目的 | 最终用途部件生产 | 设计和测试 |
| 材料范围 | 广泛,包括金属 | 主要是塑料 |
| 生产量 | Medium to high | 低 |
| 速度 | 中等到高 | 高 |
| 成本 | Higher due to material and setup | 较低,专注于快速迭代 |
| Quality Control | 严格 | 不太严格 |
多材料打印
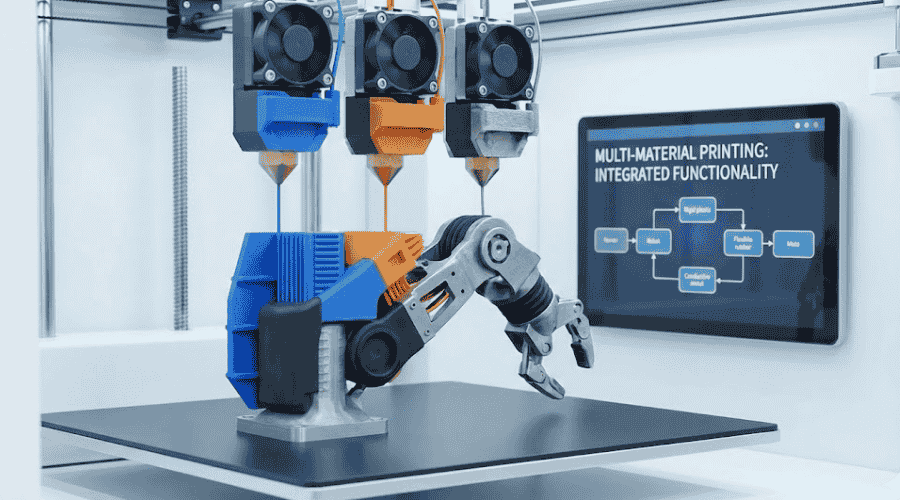
多材料打印是增材制造中的新兴趋势,能够在单一构建过程中创建具有不同材料属性的物体。这种能力对于生产需要不同机械、热或美学特性的部件至关重要。
多材料打印的好处:
- Functional Integration: By combining materials with different properties, manufacturers can create parts that perform multiple functions. For example, a single part can have both rigid and flexible sections, reducing the need for assembly and improving product performance.
- Enhanced Product Design: Designers have greater freedom to innovate, as they are no longer constrained by the limitations of single-material manufacturing. This can lead to more ergonomic and efficient designs.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Multi-material printing can reduce the number of parts needed in an assembly, decreasing production time and costs. It also minimizes the need for post-processing and assembly labor.
多材料打印的挑战:
主要挑战包括材料兼容性以及在打印过程中管理多种材料的复杂性。当前技术通常需要手动干预来切换材料,这可能会减慢生产速度并增加成本。此外,开发能够无缝集成的材料仍然是一个技术难题。
多材料与单材料打印
| 功能 | 多材料打印 | 单材料打印 |
|---|---|---|
| 复杂性 | 高复杂性,可以在一次打印中集成多个属性 | 更简单,限于一种材料的特性 |
| 定制化 | 高度定制潜力 | Limited customization options |
| 成本 | Generally higher due to material complexity | 较低,因为简单 |
| 应用 | Ideal for products requiring multiple material properties | Suitable for straightforward applications |
| 生产时间 | 更长,由于过程的复杂性 | 较短,因为工艺简单 |
| Material Compatibility | 需要仔细选择以确保兼容性 | No compatibility issues |
制造业中的人工智能
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of additive manufacturing. By enhancing design, optimizing production processes, and improving quality control, AI is helping to overcome some of the limitations of traditional manufacturing methods.
人工智能在增材制造中的应用:
- Design Optimization: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to suggest design improvements that enhance performance and reduce material usage. This capability is particularly useful in industries like aerospace and automotive, where weight reduction is crucial.
- Process Automation: AI can automate various aspects of the 3D printing process, from material selection to machine calibration. This reduces the need for skilled labor and minimizes human error, leading to more consistent production quality.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing machine data, AI can predict when maintenance is required, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment. This is particularly valuable in industrial settings where machine uptime is critical.
- Quality Assurance: AI can enhance quality control by analyzing real-time data during the printing process to detect defects or deviations from design specifications. This ensures that parts meet the required standards and reduces waste.
人工智能整合的挑战:
尽管具有潜力,将AI整合到增材制造中并非没有挑战。高昂的实施成本、数据隐私问题以及对专业知识的需求可能会阻碍采用。此外,依赖数据驱动的决策需要强大的数据管理系统和基础设施。
大幅面打印
大幅面打印代表了增材制造的重大进步,能够创造出传统3D打印技术无法实现的大型组件和结构。这一能力正在改变航空航天、建筑和汽车等行业,这些行业对大规模零件的需求普遍存在。
大幅面打印的优势
- Cost Efficiency: By producing large parts in a single print, manufacturers can reduce the need for assembly and minimize material wastage.
- Time Savings: The ability to print large objects directly reduces lead times, accelerating the production process.
- Design Flexibility: Large-format printers support complex geometries and can incorporate features that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
挑战与解决方案
尽管有其优势,大幅面打印面临着诸如在大跨度上保持结构完整性和确保材料性质一致性等挑战。机器学习在解决这些挑战中起着关键作用,通过优化打印参数和预测潜在错误。
- Material Consistency: Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets to ensure uniform material distribution and quality.
- Structural Analysis: Predictive models help in assessing the structural integrity of large prints, allowing for adjustments before production begins.
按需和去中心化生产
按需生产,也称为准时制造,利用增材制造根据需要生产物品,而不是维持大量库存。结合分散式制造——从传统的集中生产设施转向由较小的分布式制造单元组成的网络——这种方法正在重塑产品到达消费者的方式。
优势
- Inventory Reduction: By producing only what is needed, companies can significantly reduce inventory costs.
- Customization: On-demand production allows for high levels of customization, enabling manufacturers to meet specific customer requirements.
- Sustainability: Reducing overproduction minimizes waste and supports sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: By producing goods closer to the point of consumption, transportation costs and associated emissions are minimized.
- Increased Resilience: Decentralized systems are less vulnerable to disruptions, as production can be shifted between locations.
- Local Economic Benefits: Local production supports regional economies and can lead to job creation.
实施挑战
去中心化制造需要强大的物流和各生产地点之间的协调。机器学习可以通过管理供应链、预测潜在中断并确保各单元之间的无缝通信来优化这些过程。
材料限制
尽管增材制造取得了进展,材料限制仍然是一个重大挑战。与传统制造方法相比,能够有效使用的材料范围较窄。
材料多样性与特性
增材制造可用材料的多样性正在扩大,但仍然有限。金属、聚合物、陶瓷和复合材料是主要类别。每种材料类型都有其独特的特性,影响其在特定应用中的适用性。像钛和不锈钢这样的金属因其强度和耐用性而受到欢迎,使其成为航空航天和医疗应用的理想选择。聚乳酸(PLA)和丙烯腈-丁二烯-苯乙烯(ABS)等聚合物因其易用性和成本效益而受到原型制作的青睐。
然而,增材制造材料的机械性能通常与传统方法生产的材料不同。例如,增材制造的金属可能表现出各向异性,即性能随打印方向而变化。这可能影响最终产品的结构完整性和性能。
材料开发的挑战
开发增材制造的新材料是一个复杂的过程。它需要对材料科学和增材制造过程本身有深入的理解。挑战在于配制能够在打印过程中承受热和机械应力的材料,同时保持所需的特性。高温聚合物和陶瓷仍在开发中,以便更广泛地使用,这些材料对航空航天和汽车等行业至关重要,因为这些行业的零件暴露在极端条件下。
质量控制
确保增材制造产品的质量至关重要,特别是在故障可能导致严重后果的行业,如航空航天和医疗保健。增材制造的质量控制涉及多个方面,包括材料质量、尺寸精度和表面光洁度。
实时监控和反馈系统
增材制造质量控制的主要挑战之一是缺乏标准化方法。由于独特的逐层构建过程,传统的质量控制技术并不总是适用。实时监控系统利用传感器和摄像头监控打印过程,确保每一层都正确沉积。它们可以检测到翘曲、层间分层或未完全熔合等异常情况,从而在构建过程中进行纠正。
认证和标准
像ASTM国际和ISO这样的组织正在努力建立增材制造工艺和材料的综合标准。这些标准旨在确保增材制造产品符合特定的质量标准,促进其在关键应用中的使用。
后处理挑战
Post-processing is a crucial step in the AM workflow that significantly impacts the final product’s quality and functionality.
表面光洁度和尺寸精度
由于逐层构建过程,增材制造(AM)零件通常具有粗糙的表面。为了改善表面光洁度,使用了多种技术,包括打磨、喷砂和化学抛光。尺寸精度是另一个关键因素——零件通常需要进行机械加工或磨削以达到所需尺寸,这增加了生产过程的时间和成本。
机械性能增强
退火和消除应力等热处理工艺可以提高强度并减少残余应力,这对于金属零件尤其重要,因为内部应力可能导致开裂或翘曲。
支撑去除
在增材制造中,支撑结构通常是必要的,以防止零件在打印过程中变形。然而,移除这些支撑结构可能具有挑战性,尤其是对于复杂的几何形状或内部特征。使用先进算法的自动支撑移除系统正在被开发以应对这一挑战。
知识产权挑战
增材制造的激增在知识产权领域带来了独特的挑战。随着可以轻松共享和修改的数字设计文件的出现,知识产权侵权的风险增加。
保护知识产权
与传统制造不同,传统制造需要物理模具或冲模,而增材制造依赖于可以轻松全球传播的数字蓝图。传统的知识产权法律往往难以处理数字设计及其后续迭代的细微差别。
知识产权创新的机会
区块链技术提供了一种潜在的解决方案,通过提供一个安全、不可篡改的设计文件账本,帮助追踪设计的来源。随着公司开发专有技术以优化增材制造工艺,专注于独特制造方法的工艺专利变得越来越重要。
监管障碍
随着增材制造继续获得关注,监管框架难以跟上步伐。增材制造的独特方面,如其去中心化的特性和生产复杂几何形状的能力,对现有的监管标准构成了重大挑战。
当前的监管环境
目前,增材制造的监管环境是碎片化的,并且在不同地区差异显著。在医疗领域,美国FDA已经为3D打印的医疗设备制定了指导方针。在航空航天领域,FAA和EASA正在努力制定3D打印零件的标准,以确保安全性和可靠性。
监管协调的途径
以性能为基础的标准专注于结果而不是具体方法,允许更大的灵活性和创新,同时确保安全。国际合作对于创建统一的监管标准至关重要,这些标准可以减少全球市场的进入壁垒。
设计灵活性和生成设计
增材制造的一个最显著的优势是其无与伦比的设计灵活性。与传统制造方法不同,传统方法由于工具和材料的限制往往会施加约束,而增材制造可以轻松创建复杂的几何形状和定制产品。
增材制造提供的设计灵活性使得生产复杂结构成为可能,这些结构通过传统方法实现是不可能的或成本过高的。这种能力在航空航天领域特别有价值,因为它可以实现轻量化、优化的结构,在医学领域则可以用于个性化的植入物和假肢。
Generative design leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to explore a vast array of design possibilities. By inputting specific parameters and constraints, designers can generate optimized solutions that take full advantage of AM’s capabilities, leading to more innovative and efficient products.
供应链创新
增材制造通过使按需制造更接近消费点来革新供应链动态。公司可以降低运输成本,缩短交货时间,并减少库存水平。按需生产零件的能力也降低了与地缘政治紧张局势、自然灾害或流行病相关的供应链中断风险。
ISO认证
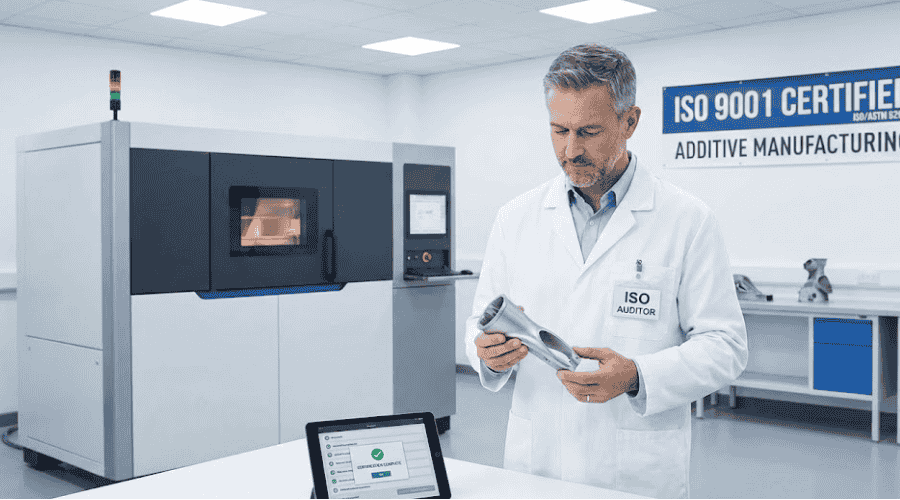

增材制造中的ISO认证确保了整个行业的一致质量和安全标准。它提供了最佳实践的框架,帮助制造商实现最佳性能和可靠性。
关键ISO标准
- ISO/ASTM 52900: Provides a comprehensive overview of terminology used in additive manufacturing.
- ISO/ASTM 52901:概述了工艺和设备资格认证的要求。
- ISO/ASTM 52915:规定了增材制造中使用的数字数据的要求。
获得ISO认证涉及严格的评估和对相关标准的合规。其好处包括增强信誉、提高客户信心和进入新市场的机会。
常见问题解答
增材制造如何提高效率?
增材制造通过更快的打印技术、新的高性能材料和先进的设计软件提高了效率。这些创新有助于减少生产时间和浪费,使制造商能够更快速和经济地生产高质量的零件。
增材制造在供应链创新中扮演什么角色?
增材制造实现了去中心化生产,增强了定制化和灵活性,并降低了与中断相关的风险。通过允许在更接近消费点进行按需制造,公司可以降低运输成本,缩短交货时间,并保持供应的连续性。
为什么ISO认证在增材制造中很重要?
ISO certification ensures consistent quality and safety standards, facilitates international trade, and
enhances credibility. By adhering to globally recognized standards, manufacturers can assure clients of theircommitment to quality and gain a competitive edge in the global market.
增材制造的未来充满希望,具有改变行业和重新定义可能性边界的巨大潜力。知识产权保护、监管框架、材料开发、质量控制和后处理仍然是关键挑战。然而,持续的研究和技术进步正在解决这些问题。
通过制定创新的知识产权保护策略、促进监管协调、接受设计灵活性以及通过ISO认证确保质量,公司可以解锁新的增长和创新机会。随着技术的不断发展,行业利益相关者、监管机构和学术界之间的合作将是塑造增材制造在全球经济中发挥核心作用的未来的关键。
For those interested in exploring related topics, consider reading our guides on “How AI is Transforming Manufacturing,” “The Benefits of Multi-Material 3D Printing,” and “Understanding Large-Format 3D Printing.”