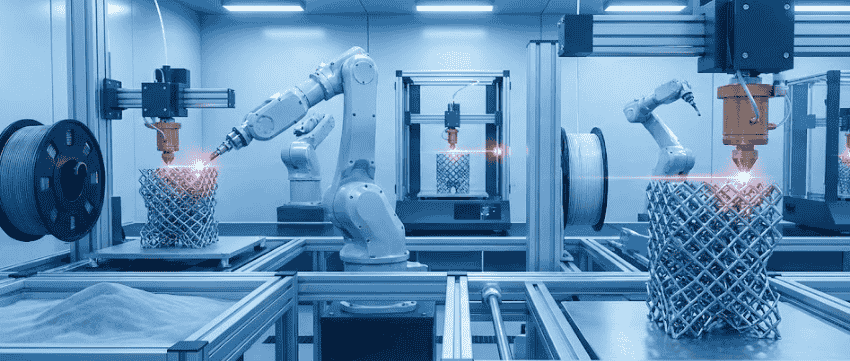
Additive manufacturing, commonly known as 3D printing, is revolutionizing the industrial landscape. As industries strive for efficiency and innovation, the demand for advanced manufacturing techniques is increasing. However, the rapid evolution of this technology presents challenges that must be addressed to fully harness its potential.
빠른 수정 요약 표
| 문제 | Quick Fix | 장기적인 해결책 | 영향 | 예시 산업 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| High material costs | 재활용 재료 사용 | 비용 효율적인 재료 개발 | Reduced production costs | 자동차 |
| 제한된 다중 재료 기능 | Invest in hybrid printers | 재료 호환성 연구 | Enhanced product functionality | 항공우주 |
| 느린 생산 속도 | Optimize printing parameters | 더 빠른 인쇄 기술 개발 | 처리량 증가 | Consumer Electronics |
| 설계 복잡성 제한사항 | AI 기반 디자인 도구 사용 | Develop advanced CAD software | 더 큰 디자인 유연성 | 의료 기기 |
| Lack of skilled workforce | 교육 프로그램 시행 | 자동화를 위한 AI 통합 | Increased efficiency and innovation | 일반 제조 |
산업용 3D 프린팅
Industrial 3D printing, a subset of additive manufacturing, is transforming production processes across sectors. Unlike traditional manufacturing, which often involves subtractive processes, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, reducing waste and enabling complex geometries. This technology is particularly beneficial for industries requiring customized solutions, such as aerospace, automotive, and healthcare.
산업용 3D 프린팅의 장점:
- Customization and Complexity: Industrial 3D printing allows for the creation of complex geometries that are difficult or impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. This capability is particularly valuable in industries like aerospace, where intricate designs can lead to improved performance and efficiency.
- Reduced Waste: Traditional manufacturing processes often result in significant material waste. In contrast, additive manufacturing uses only the material necessary to build an object, leading to more sustainable production practices.
- Rapid Prototyping and Production: The ability to quickly produce prototypes accelerates the design and testing phases of product development. This speed also translates to faster production times for end-use parts, reducing time-to-market.
- Cost Efficiency for Low Volume Production: For small batch productions, 3D printing can be more cost-effective than traditional methods, which often require expensive tooling and setup.
- Supply Chain Simplification: By enabling on-demand production, 3D printing can reduce the need for large inventories and complex supply chains, lowering costs and increasing responsiveness to market demands.
산업용 3D 프린팅의 도전 과제:
Despite its advantages, industrial 3D printing faces several challenges. High material costs, limited material options, and slower production speeds compared to traditional methods can hinder widespread adoption. Additionally, quality control and standardization remain significant hurdles.
비교 표: 산업용 vs 프로토타입 3D 프린팅
| 기능 | Industrial 3D Printing | 프로토타입 3D 프린팅 |
|---|---|---|
| 목적 | End-use part production | 설계 및 테스트 |
| 재료 범위 | Broad, including metals | 주로 플라스틱 |
| 생산량 | Medium to high | 낮음 |
| 속도 | 중간에서 높음 | 높음 |
| 비용 | Higher due to material and setup | 낮음, 빠른 반복에 중점 |
| Quality Control | 엄격한 | 덜 엄격한 |
다중 소재 프린팅
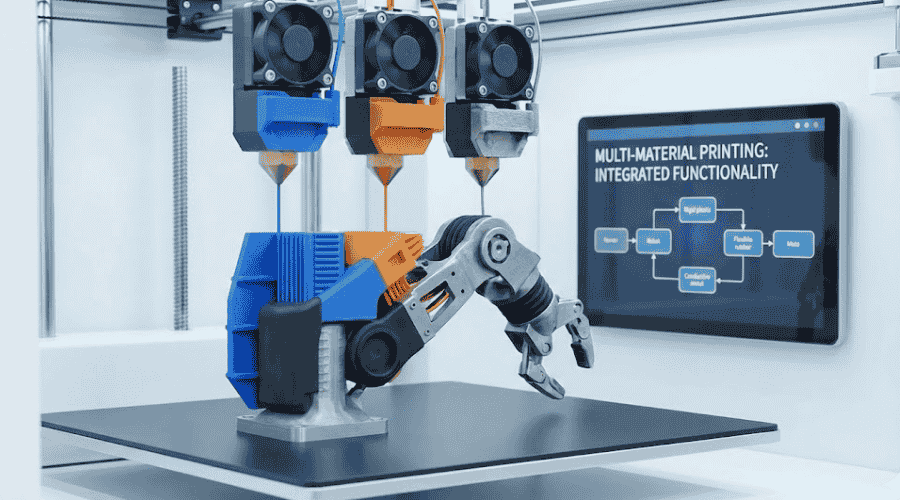
Multi-material printing is an emerging trend in additive manufacturing, enabling the creation of objects with varied material properties in a single build process. This capability is crucial for producing parts that require different mechanical, thermal, or aesthetic characteristics.
다중 재료 프린팅의 이점:
- Functional Integration: By combining materials with different properties, manufacturers can create parts that perform multiple functions. For example, a single part can have both rigid and flexible sections, reducing the need for assembly and improving product performance.
- Enhanced Product Design: Designers have greater freedom to innovate, as they are no longer constrained by the limitations of single-material manufacturing. This can lead to more ergonomic and efficient designs.
- Cost and Time Efficiency: Multi-material printing can reduce the number of parts needed in an assembly, decreasing production time and costs. It also minimizes the need for post-processing and assembly labor.
다중 재료 프린팅의 도전 과제:
The primary challenges include material compatibility and the complexity of managing multiple materials during the printing process. Current technology often requires manual intervention to switch materials, which can slow down production and increase costs. Additionally, developing materials that can seamlessly integrate with each other remains a technical hurdle.
다중 재료 vs 단일 재료 프린팅
| 기능 | Multi-Material Printing | 단일 소재 인쇄 |
|---|---|---|
| 복잡성 | High complexity, can integrate multiple properties in one print | Simpler, limited to the properties of one material |
| 사용자 정의 | 높은 맞춤화 가능성 | Limited customization options |
| 비용 | Generally higher due to material complexity | 단순함으로 인해 더 낮음 |
| 응용 분야 | Ideal for products requiring multiple material properties | Suitable for straightforward applications |
| 생산 시간 | Longer, due to complexity of processes | 공정이 단순하여 더 짧아짐 |
| Material Compatibility | 호환성을 보장하기 위해 신중한 선택 필요 | No compatibility issues |
제조업의 AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is playing a transformative role in the field of additive manufacturing. By enhancing design, optimizing production processes, and improving quality control, AI is helping to overcome some of the limitations of traditional manufacturing methods.
적층 제조에서의 AI 응용:
- Design Optimization: AI algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data to suggest design improvements that enhance performance and reduce material usage. This capability is particularly useful in industries like aerospace and automotive, where weight reduction is crucial.
- Process Automation: AI can automate various aspects of the 3D printing process, from material selection to machine calibration. This reduces the need for skilled labor and minimizes human error, leading to more consistent production quality.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing machine data, AI can predict when maintenance is required, reducing downtime and extending the lifespan of equipment. This is particularly valuable in industrial settings where machine uptime is critical.
- Quality Assurance: AI can enhance quality control by analyzing real-time data during the printing process to detect defects or deviations from design specifications. This ensures that parts meet the required standards and reduces waste.
AI 통합의 과제:
Despite its potential, integrating AI into additive manufacturing is not without challenges. High implementation costs, data privacy concerns, and the need for specialized expertise can hinder adoption. Additionally, the reliance on data-driven decision-making requires robust data management systems and infrastructure.
대형 포맷 프린팅
Large-format printing represents a significant advancement in additive manufacturing, allowing for the creation of larger components and structures that were previously unfeasible with traditional 3D printing technologies. This capability is transforming industries such as aerospace, construction, and automotive, where the demand for large-scale parts is prevalent.
대형 포맷 프린팅의 장점
- Cost Efficiency: By producing large parts in a single print, manufacturers can reduce the need for assembly and minimize material wastage.
- Time Savings: The ability to print large objects directly reduces lead times, accelerating the production process.
- Design Flexibility: Large-format printers support complex geometries and can incorporate features that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods.
도전과 해결책
Despite its advantages, large-format printing faces challenges such as maintaining structural integrity over large spans and ensuring consistent material properties. Machine learning plays a crucial role in addressing these challenges by optimizing print parameters and predicting potential errors.
- Material Consistency: Machine learning algorithms can analyze vast datasets to ensure uniform material distribution and quality.
- Structural Analysis: Predictive models help in assessing the structural integrity of large prints, allowing for adjustments before production begins.
주문형 및 분산형 생산
On-demand production, also known as just-in-time manufacturing, leverages additive manufacturing to produce items as needed, rather than maintaining large inventories. Combined with decentralized manufacturing—a shift from traditional centralized production facilities to a network of smaller, distributed manufacturing units—this approach is reshaping how products reach consumers.
이점
- Inventory Reduction: By producing only what is needed, companies can significantly reduce inventory costs.
- Customization: On-demand production allows for high levels of customization, enabling manufacturers to meet specific customer requirements.
- Sustainability: Reducing overproduction minimizes waste and supports sustainable manufacturing practices.
- Reduced Transportation Costs: By producing goods closer to the point of consumption, transportation costs and associated emissions are minimized.
- Increased Resilience: Decentralized systems are less vulnerable to disruptions, as production can be shifted between locations.
- Local Economic Benefits: Local production supports regional economies and can lead to job creation.
구현 과제
Decentralized manufacturing requires robust logistics and coordination between various production sites. Machine learning can optimize these processes by managing supply chains, predicting potential disruptions, and ensuring seamless communication between units.
소재 제한
Despite its advancements, material limitations remain a significant challenge in additive manufacturing. The range of materials that can be effectively used is narrower compared to traditional manufacturing methods.
재료 다양성과 특성
The diversity of materials available for AM is expanding but still limited. Metals, polymers, ceramics, and composites are the primary categories. Each material type has unique properties that influence its suitability for specific applications. Metals like titanium and stainless steel are popular for their strength and durability, making them ideal for aerospace and medical applications. Polymers such as PLA and ABS are favored for prototyping due to their ease of use and cost-effectiveness.
However, the mechanical properties of AM materials often differ from those produced by conventional methods. For instance, AM metals can exhibit anisotropy, where properties vary based on the direction of the print. This can affect the structural integrity and performance of the final product.
재료 개발의 도전 과제
Developing new materials for AM is a complex process. It requires a deep understanding of material science and the AM process itself. The challenge lies in formulating materials that can withstand the thermal and mechanical stresses during printing while maintaining desired properties. High-temperature polymers and ceramics are still under development for broader use, and these materials are crucial for industries like aerospace and automotive, where parts are exposed to extreme conditions.
품질 관리
Ensuring the quality of AM products is critical, particularly in industries where failure can have severe consequences, such as aerospace and healthcare. Quality control in AM involves several aspects, including material quality, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish.
실시간 모니터링 및 피드백 시스템
One of the primary challenges in AM quality control is the lack of standardized methods. Traditional quality control techniques are not always applicable due to the unique layer-by-layer construction process. Real-time monitoring systems utilize sensors and cameras to monitor the printing process, ensuring that each layer is correctly deposited. They can detect anomalies such as warping, layer delamination, or incomplete fusion, allowing for corrective actions during the build process.
인증 및 표준
Organizations like ASTM International and ISO are working towards establishing comprehensive standards for AM processes and materials. These standards aim to ensure that AM products meet specific quality criteria, facilitating their use in critical applications.
후처리 과제
Post-processing is a crucial step in the AM workflow that significantly impacts the final product’s quality and functionality.
표면 마감 및 치수 정확도
AM parts often have a rough surface due to the layer-by-layer construction process. Several techniques are used to improve surface finish, including sanding, bead blasting, and chemical smoothing. Dimensional accuracy is another critical factor—parts often require machining or grinding to achieve the desired dimensions, adding time and cost to the production process.
기계적 특성 향상
Heat treatment processes like annealing and stress relieving improve strength and reduce residual stresses, particularly important for metal parts where internal stresses can lead to cracking or warping.
지지대 제거
Support structures are often necessary in AM to prevent part deformation during printing. However, their removal can be challenging, especially for complex geometries or internal features. Automated support removal systems using advanced algorithms are being developed to address this challenge.
지적 재산권 문제
The surge in additive manufacturing presents unique challenges in the realm of intellectual property (IP). With the advent of digital design files that can be shared and modified effortlessly, the risk of IP infringement escalates.
지적 재산 보호
Unlike traditional manufacturing, where physical molds or dies are necessary, AM relies on digital blueprints that can be disseminated globally with minimal effort. Traditional IP laws are often ill-equipped to address the nuances of digital designs and their subsequent iterations.
지적 재산 혁신 기회
Blockchain technology offers a potential solution by providing a secure, immutable ledger for design files, helping track the provenance of a design. Process patents focusing on unique fabrication methods are becoming increasingly relevant as companies develop proprietary techniques to optimize AM processes.
규제 장벽
As additive manufacturing continues to gain traction, regulatory frameworks struggle to keep pace. The unique aspects of AM, such as its decentralized nature and the ability to produce complex geometries, pose significant challenges to existing regulatory standards.
현재 규제 환경
Currently, the regulatory environment for additive manufacturing is fragmented and varies significantly across regions. In the medical field, the U.S. FDA has established guidelines for 3D-printed medical devices. In aerospace, the FAA and EASA are working to develop standards for 3D-printed parts to ensure safety and reliability.
규제 조화의 경로
Performance-based standards, which focus on outcomes rather than specific methods, allow for greater flexibility and innovation while ensuring safety. International cooperation is essential for creating harmonized regulatory standards that reduce barriers to entry in the global market.
설계 유연성과 생성적 설계
One of the most significant advantages of additive manufacturing is its unparalleled design flexibility. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods, which often impose constraints due to tooling and material limitations, AM allows for the creation of complex geometries and customized products with ease.
The design flexibility offered by AM enables the production of intricate structures that would be impossible or prohibitively expensive to achieve with conventional methods. This capability is particularly valuable in aerospace for lightweight, optimized structures and in medicine for personalized implants and prosthetics.
Generative design leverages artificial intelligence and machine learning to explore a vast array of design possibilities. By inputting specific parameters and constraints, designers can generate optimized solutions that take full advantage of AM’s capabilities, leading to more innovative and efficient products.
공급망 혁신
Additive manufacturing is revolutionizing supply chain dynamics by enabling on-demand manufacturing closer to the point of consumption. Companies can reduce transportation costs, decrease lead times, and minimize inventory levels. The ability to produce parts on-demand also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions from geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, or pandemics.
ISO 인증
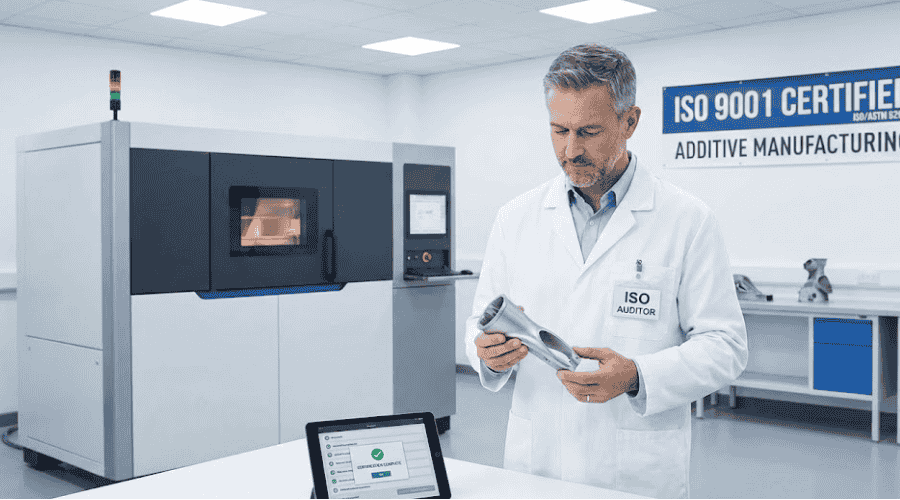

ISO certification in additive manufacturing ensures consistent quality and safety standards across the industry. It provides a framework for best practices, helping manufacturers achieve optimal performance and reliability.
주요 ISO 표준
- ISO/ASTM 52900: Provides a comprehensive overview of terminology used in additive manufacturing.
- ISO/ASTM 52901: 프로세스 및 장비의 자격 요건을 설명합니다.
- ISO/ASTM 52915: 적층 제조에서 사용되는 디지털 데이터의 요구 사항을 명시합니다.
Achieving ISO certification involves rigorous assessment and compliance with relevant standards. The benefits include enhanced credibility, improved customer confidence, and access to new markets.
자주 묻는 질문
적층 제조가 효율성을 어떻게 향상시키고 있는가?
Additive manufacturing improves efficiency through faster printing technologies, new high-performance materials, and advanced design software. These innovations contribute to reduced production times and waste, enabling manufacturers to produce high-quality parts more quickly and cost-effectively.
첨가제 제조가 공급망 혁신에서 어떤 역할을 하는가?
AM enables decentralized production, enhances customization and flexibility, and mitigates risks associated with disruptions. By allowing on-demand manufacturing closer to the point of consumption, companies can reduce transportation costs, decrease lead times, and maintain continuity of supply.
첨가제 제조에서 ISO 인증이 중요한 이유는 무엇인가?
ISO certification ensures consistent quality and safety standards, facilitates international trade, and
enhances credibility. By adhering to globally recognized standards, manufacturers can assure clients of theircommitment to quality and gain a competitive edge in the global market.
The future of additive manufacturing is promising, with significant potential to transform industries and redefine the boundaries of what is possible. Key challenges remain in intellectual property protection, regulatory frameworks, material development, quality control, and post-processing. However, ongoing research and technological advancements are addressing these issues.
By developing innovative IP protection strategies, fostering regulatory harmonization, embracing design flexibility, and ensuring quality through ISO certification, companies can unlock new opportunities for growth and innovation. As the technology continues to evolve, collaboration between industry stakeholders, regulatory bodies, and academia will be essential in shaping a future where additive manufacturing plays a central role in the global economy.
For those interested in exploring related topics, consider reading our guides on “How AI is Transforming Manufacturing,” “The Benefits of Multi-Material 3D Printing,” and “Understanding Large-Format 3D Printing.”